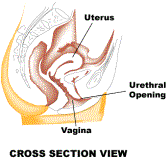
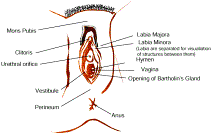
FEMALE EXTERNAL GENITALIA The external female genitals are collectively referred to as The Vulva. All of the words below are part of the vulva. External View: The Vulva The Parts of the Vulva | Mons Veneris | Labia
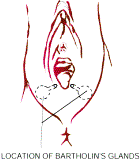
Majora | Labia Minora | The mons veneris, Latin for "hill of Venus" is the pad of fat that covers the pubic bone below the abdomen but above the labia. The mons is one of the sexually sensitive zones in women and protects the pubic bone from the impact of sexual intercourse. The labia majora are the outer lips of the vulva, pads of fat again that wrap around the vulva from the mons to the perineum. The labia minora are the inner lips of the vulva, thin stretches of tissue within the labia majora that fold and protect the vagina, urethra, and clitoris. Both the inner and outer labia are quite sensitive to touch and pressure. The clitoris, visible in picture as the small white oval at the top of the labia minora, is a small body of spongy tissue that is highly sexually sensitive. The clitoris is protected by the clitoral hood, or female prepuce, a covering of tissue similar to the labia minora. The opening to the urethra is just below the clitoris. It is not related to sex or reproduction, but is instead the passage for urine. The opening of the urethra (urethral meatus) opens into the vestibule between the clitoris and vagina. Just behind it on either side can sometimes be seen the openings of the para urethral or Skene’s glands. The openings of Bartholin’s glands are located towards the back on either side of the vaginal opening, but the glands are not usually visible. Bartholin’s glands themselves are situated more towards the inside.
The urethra is connected to the bladder. Because the urethra is so close to the anus, women should always wipe themselves from front to back to avoid infecting the vagina and urethra with bacteria. The above illustrations show the area between the labia minora. From top to bottom can be clearly seen the clitoris, urethral opening, and vaginal opening. Normally hymen, is a membrane that partially covers the opening. The hymen is the traditional "symbol" of virginity, although being a very thin membrane, it can be torn by vigorous exercise or the insertion of a tampon. The perineum is the short stretch of skin starting at the bottom of the vulva and extending to the anus. The perineum in women often tears during birth to accommodate passage of the child, and this is apparently natural. Some physicians may cut the perineum preemptively on the grounds that the "tearing" may be more harmful than a precise scalpel, but statistics show that such cutting in fact may increase the potential for infection. |